Tense
What is Tense?
Simply put, tenses are grammatical forms of verbs used to indicate the time of an action, event or state of something or someone in a sentence.
In English, there are three primary tenses: the past tense, the present tense, and the future tense. Each of these tenses can be further divided into four aspects: simple, continuous (or progressive), perfect, and perfect continuous.
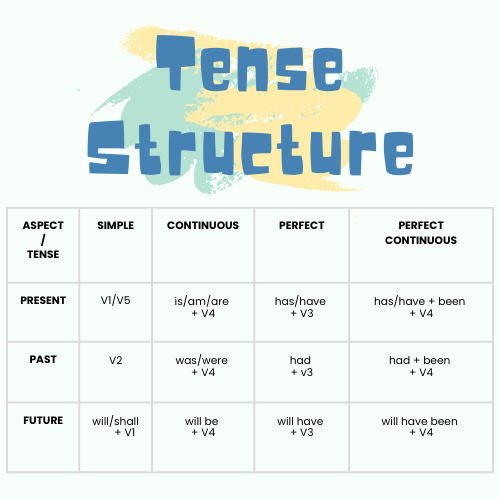
Tense Structure
| V1 | V2 | V3 | V4 | V5 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Base/Present | Past | Past Participle | Present Participle | Present Singular | |
| REGULAR | walk | walked | walked | walking | walks |
| IRREGULAR | go | went | gone | going | goes |
Present
| Simple | Continuous | Perfect | Perfect Continuous | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V1/V5 | am/is/are + V4 | have/has + V3 | has/have been + V4 | |
| REGULAR | talk/s | talking | have/has talked | have/has been talking |
| IRREGULAR | eat/s | eating | have/has eaten | have/has been eating |
Simple Present: Used to describe actions or events that are happening now, habitual actions, general truths, and scheduled events in the future.
Example: “I write a letter.” (happening now) / “She plays the piano.” (habitual action) / “The sun rises in the east.” (general truth) / “The train departs tomorrow.” (scheduled future event)
Present Continuous/Progressive: Used to describe actions that are currently in progress at the time of speaking or to describe future plans or arrangements.
Example: “I am writing a letter.” (currently in progress) / “He is meeting his friends tomorrow.” (future arrangement)
Present Perfect: Used to describe actions that started in the past and have a connection to the present.
Example: “I have seen that movie before.”
Present Perfect Continuous/Progressive: Used to describe actions that started in the past, are still continuing, and have a connection to the present.
Example: “She has been studying for her exams.”
Past
| Simple | Continuous | Perfect | Perfect Continuous | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| V2 | “to be” (was/were) + V4 | had + V3 | had been + V4 | |
| REGULAR | talked | was/were talking | had talked | had been talking |
| IRREGULAR | ate | was/were eating | had eaten | had been eating |
Simple Past: Used to describe actions or events that have already happened in the past.
Example: “She wrote a letter yesterday.”
Past Continuous/Progressive: Used to describe actions that were ongoing at a specific point in the past.
Example: “They were watching a movie when I arrived.”
Past Perfect: Used to describe actions that were completed before a specific point in the past.
Example: “He had already left when I arrived.”
Past Perfect Continuous/Progressive: Used to describe actions that were ongoing for a period before a specific point in the past.
Example: “They had been waiting for hours before the concert started.”
Future
| Simple | Continuous | Perfect | Perfect Continuous | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| will + V1 | will be + V4 | will + have + V3 | will + have been + V4 | |
| REGULAR | will + talk | will be talking | will have talked | will have been talking |
| IRREGULAR | will + eat | will be eating | will have eaten | will have been eating |
Simple Future: Used to describe actions that will happen in the future.
Example: “They will visit their grandparents next week.”
Future Continuous/Progressive: Used to describe actions that will be in progress at a specific time in the future.
Example: “I will be studying at 9 PM tomorrow.”
Future Perfect: Used to describe actions that will be completed before a specific time in the future.
Example: “By next month, I will have finished my project.”
Future Perfect Continuous/Progressive: Used to describe actions that will have been ongoing and completed before a specific time in the future.
Example: “He will have been working for ten years by the end of this month.”



